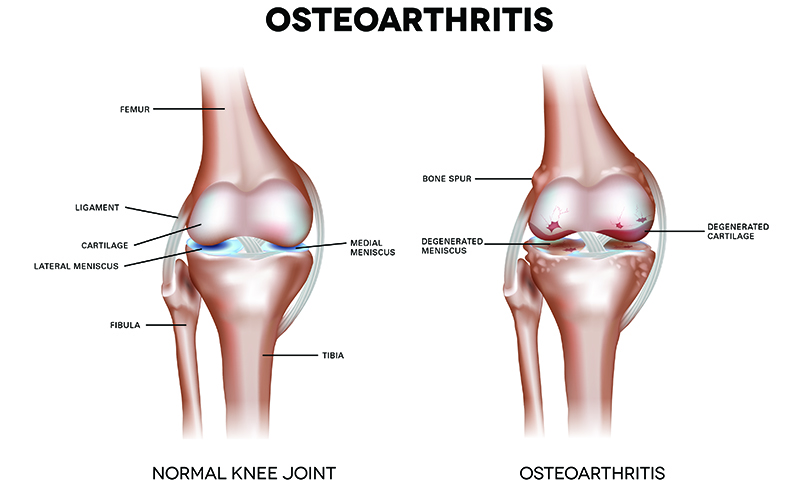
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent joint disorder worldwide and is associated with significant pain and disability.6 It is a progressive disease that can affect any joint but most often involves the weight bearing joints.

Aging
As a person gets older, the body’s ability to heal damaged or lost cartilage decreases
Joint injury
Younger people can also develop OA due to joint injury, for example, athletes who have suffered from a sports-related knee injury
Heredity
If there is a family history of OA, the risk for developing the disease increases
Repeated joint stress
Excess weight or overuse of the joint causes stress or increased wear and tear on the joint
Muscle weakness
If the muscles that surround the joint are weak, added stress is placed on the joint
Joint disorder
If there is a joint malformation or a genetic defect in the joint Cartilage
Joints that can be affected by OA
A significant proportion of the world’s population is afflicted by OA of the knee, and the disease ranks as either the top or second leading cause of disability.
Joints that can be affected include:
- Knees
- Hips
- Ankles
- Spine – neck and lower back
- Hands – fingers and thumbs
- Shoulders
Symptoms of OA
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Limitation or loss of physical function
- A crackling sound when moving the joint
Think you have OA?
Living with osteoarthritis can not only be painful, but also discouraging. Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of knee pain. Patients who think they may have OA should talk to their doctor. Although there is no cure for the disease, the sooner patients start treatment, the more manageable their OA may become, and the longer they may be able to delay surgery or total knee replacement.
Why Cingal